Thinning hair is a common concern for individuals of all ages and genders. Whether it’s due to genetics, aging, hormonal changes, or lifestyle factors, experiencing thinning hair can be distressing and impact self-esteem. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of thinning hair is crucial for early intervention and effective management. In this article, we delve into what thinning hair looks like, exploring its various manifestations, causes, and potential treatment options.
What Does Thinning Hair Look Like?
Thinning hair can manifest in several ways, and its appearance may vary depending on the underlying cause and individual factors. Here are some common signs and symptoms to look out for:
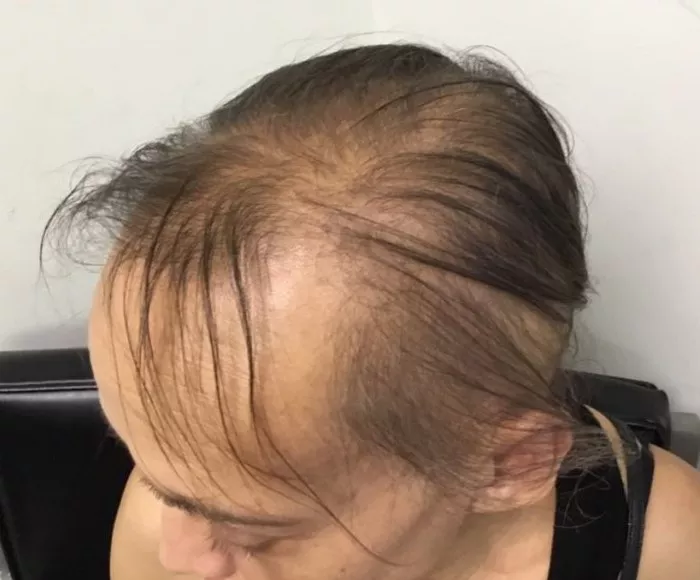
1. Decreased Volume: One of the earliest signs of thinning hair is a noticeable decrease in volume. Hair may appear flat and lackluster, lacking the bounce and fullness associated with healthy hair.
2. Widening Part: As hair begins to thin, the part line may widen, becoming more prominent. This widening is often due to decreased hair density, making the scalp more visible.
3. Increased Scalp Visibility: Thinning hair often results in increased visibility of the scalp, especially in areas where hair is naturally thinner, such as the temples and crown. This may be particularly noticeable in bright lighting or when hair is pulled back.
4. Hair Shedding: Excessive hair shedding, known as telogen effluvium, is another common sign of thinning hair. Individuals may notice more hair than usual falling out during activities such as washing, brushing, or styling.
5. Reduced Hair Diameter: Thinning hair may also be characterized by a reduction in hair diameter, resulting in finer, less robust strands. This can contribute to a wispy or frail appearance, particularly towards the ends of the hair shafts.
6. Patchy Hair Loss: In some cases, thinning hair may progress to more pronounced hair loss, leading to patchy or diffuse areas of baldness on the scalp. This can be a distressing experience and may require prompt medical attention.
7. Changes in Hair Texture: Thinning hair may also exhibit changes in texture, becoming dry, brittle, or prone to breakage. These changes can further contribute to the overall appearance of hair thinning.
8. Slower Hair Growth: Individuals with thinning hair may notice that their hair grows more slowly than usual, leading to difficulty in achieving desired length or fullness.
Causes of Thinning Hair
Thinning hair can be attributed to various factors, ranging from genetics to lifestyle choices. Understanding the underlying causes is essential for implementing targeted treatment strategies. Some common causes of thinning hair include:
1. Genetics: Hereditary factors play a significant role in determining hair thickness and density. Individuals with a family history of thinning hair or pattern baldness are more likely to experience similar issues themselves.
2. Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those occurring during puberty, pregnancy, childbirth, or menopause, can contribute to thinning hair. Hormonal imbalances, such as an excess of androgens or a deficiency of estrogen, can disrupt the hair growth cycle and lead to hair loss.
3. Aging: As individuals age, the rate of hair growth slows down, and hair follicles may become less active, resulting in thinner, less abundant hair. Age-related changes in hormone levels and decreased blood flow to the scalp can also contribute to hair thinning.
4. Nutritional Deficiencies: Poor nutrition, particularly deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals such as iron, zinc, and vitamin D, can negatively impact hair health and contribute to thinning.
5. Stress: Chronic stress can disrupt the hair growth cycle and lead to increased shedding and thinning. This type of hair loss, known as telogen effluvium, is often temporary but can become chronic if stress levels remain high.
6. Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases, and alopecia areata, can cause hair thinning or loss. Treating the underlying medical condition is essential for managing hair-related symptoms.
7. Medications: Some medications, including chemotherapy drugs, hormone therapies, and certain antidepressants, can cause hair thinning or loss as a side effect. Consulting with a healthcare provider about alternative treatments or adjusting medication dosage may help mitigate this issue.
8. Overstyling: Excessive heat styling, chemical treatments, and tight hairstyles can damage the hair shaft and lead to breakage and thinning over time. Limiting the use of heat tools, opting for gentle hair care products, and avoiding tight hairstyles can help preserve hair health.
Treatment Options for Thinning Hair
Effective management of thinning hair often requires a comprehensive approach targeting underlying causes and promoting hair growth and health. While individual treatment plans may vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of thinning, some common treatment options include:
1. Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter topical treatments containing minoxidil (Rogaine) can help stimulate hair growth and increase hair density in individuals with androgenetic alopecia. Prescription-strength formulations may be recommended for more severe cases.
2. Prescription Medications: Oral medications such as finasteride (Propecia) may be prescribed to men with androgenetic alopecia to block the conversion of testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone that contributes to hair loss.
3. Nutritional Supplements: Supplementing with vitamins and minerals essential for hair health, such as biotin, iron, and zinc, may help support hair growth and thickness. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements to avoid potential interactions or adverse effects.
4. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP therapy involves injecting platelet-rich plasma derived from the patient’s blood into the scalp to stimulate hair follicle activity and promote hair growth. This treatment may be beneficial for individuals with androgenetic alopecia or other types of hair loss.
5. Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): LLLT devices, such as laser combs or helmets, emit low-level laser light to the scalp, purportedly stimulating hair follicles and promoting hair growth. While research on the efficacy of LLLT for treating hair loss is mixed, some individuals may experience positive results with regular use.
6. Hair Transplant Surgery: In cases of advanced hair loss or baldness, hair transplant surgery may be considered. This procedure involves transplanting hair follicles from areas of the scalp with healthy hair growth to areas experiencing thinning or baldness.
7. Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting healthy lifestyle habits, such as eating a balanced diet, managing stress levels, avoiding smoking, and practicing good hair care hygiene, can help support overall hair health and minimize further thinning.
Conclusion
Thinning hair is a common concern affecting individuals of all ages and genders, with various causes ranging from genetics to lifestyle factors. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of thinning hair is essential for early intervention and effective management. By understanding the underlying causes and implementing targeted treatment strategies, individuals can take proactive steps to promote hair growth and maintain healthy, voluminous hair. Consulting with a healthcare provider or dermatologist is recommended for personalized evaluation and treatment recommendations tailored to individual needs.