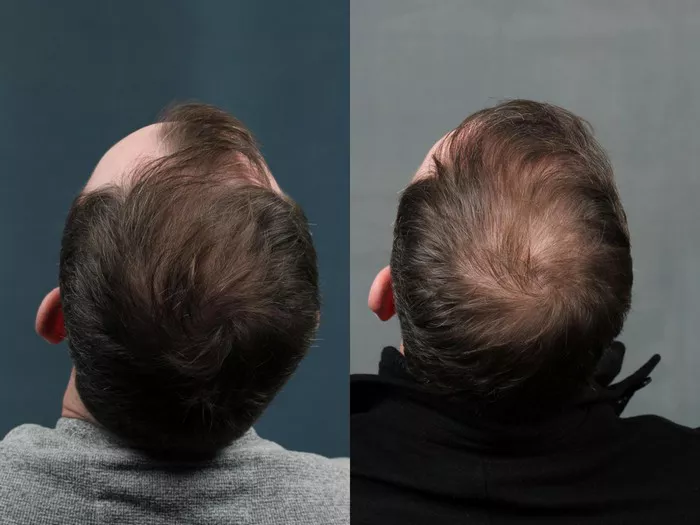
Hair transplantation has become an increasingly popular solution for individuals struggling with hair loss. Whether due to genetics, aging, or other factors, the desire to regain a full head of hair prompts many to explore this surgical procedure. However, one common concern among those considering or undergoing hair transplant surgery is the possibility of transplanted hair falling out. Understanding the intricacies of the procedure and the natural hair growth cycle can provide clarity on this matter.
The Science Behind Hair Transplantation
To comprehend why transplanted hair may fall out, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamentals of the procedure itself. Hair transplantation involves relocating hair follicles from a donor site, typically the back or sides of the scalp, to the recipient area, which is experiencing hair loss. The two primary techniques used in hair transplantation are follicular unit transplantation (FUT) and follicular unit extraction (FUE).
In FUT, a strip of tissue containing hair follicles is harvested from the donor area and then dissected into individual follicular units for transplantation. On the other hand, FUE involves extracting individual follicular units directly from the donor site using a specialized punch tool. Once the follicles are harvested, they are meticulously implanted into tiny incisions made in the recipient area, following the natural hair growth pattern.
Understanding the Hair Growth Cycle
Hair growth occurs in a cyclical process consisting of three phases: anagen, catagen, and telogen.
1. Anagen Phase: This is the active growth phase, during which hair follicles produce hair shafts. The duration of the anagen phase varies from person to person and determines the length of the hair.
2. Catagen Phase: Also known as the transitional phase, catagen marks the end of active hair growth. The hair follicle regresses, detaching from the blood supply, and the hair shaft stops growing.
3. Telogen Phase: Telogen is the resting phase, during which the hair follicle remains dormant. Eventually, the old hair is shed, and the follicle re-enters the anagen phase to begin a new cycle.
Understanding this cycle is crucial in comprehending the dynamics of hair transplantation and why transplanted hair may fall out initially.
The Shedding Phase: Telogen Effluvium
It’s not uncommon for individuals who undergo hair transplant surgery to experience a temporary shedding of transplanted hair, typically occurring within the first few weeks to months following the procedure. This shedding, known as telogen effluvium, is a natural part of the hair growth cycle and is not indicative of the procedure’s failure. Instead, it’s the body’s response to the trauma of surgery.
During the transplantation process, the hair follicles undergo stress and shock due to the harvesting and implantation process. This trauma can trigger the affected hair follicles to enter the telogen phase prematurely, leading to shedding. While this shedding may cause concern for patients, it is essential to understand that it is a transient phase, and the transplanted follicles remain viable beneath the scalp.
The Regrowth Process
Following the shedding phase, the transplanted hair follicles gradually enter the anagen phase, initiating the regrowth process. It’s essential to note that hair growth is a gradual process, and visible results may not be apparent immediately. It may take several months for the newly transplanted hair to start growing visibly and blending seamlessly with the existing hair.
As the hair continues to grow, patients will notice a gradual improvement in hair density and coverage in the recipient area. However, it’s essential to manage expectations and understand that achieving the desired results may require patience and multiple sessions, particularly for individuals with extensive hair loss.
Factors Influencing Transplanted Hair Growth
Several factors can influence the success of hair transplantation and the subsequent growth of transplanted hair:
1. Patient’s Age: Younger patients tend to have better outcomes with hair transplantation as they have a higher likelihood of retaining donor hair quality and experiencing robust hair growth.
2. Extent of Hair Loss: The degree of hair loss and the availability of donor hair can impact the overall results of the transplantation. Individuals with advanced hair loss may require multiple sessions to achieve satisfactory coverage.
3. Quality of Donor Hair: The quality and density of the donor hair play a significant role in determining the success of the transplantation. Healthy, thick hair follicles yield better results.
4. Postoperative Care: Following proper postoperative care instructions provided by the surgeon is crucial for ensuring optimal healing and hair growth. This includes avoiding activities that may traumatize the scalp, following a recommended skincare routine, and attending follow-up appointments as scheduled.
5. Underlying Health Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as autoimmune disorders or hormonal imbalances, can affect hair growth and may influence the outcome of hair transplantation.
By considering these factors and adhering to postoperative guidelines, patients can enhance their chances of achieving favorable outcomes with hair transplantation.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While some shedding and temporary hair loss are normal following hair transplant surgery, certain signs may indicate complications or suboptimal results. Patients should consult their surgeon if they experience:
1. Excessive or prolonged shedding beyond the expected timeframe.
2. Signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or drainage from the transplant site.
3. Delayed or impaired healing of the donor or recipient area.
4. Uneven or patchy growth of transplanted hair.
It’s essential to address any concerns promptly to ensure appropriate intervention and optimize the results of the transplantation.
Conclusion
Hair transplantation is a viable solution for individuals seeking to restore hair density and confidence. While it’s normal for transplanted hair to fall out temporarily following the procedure, understanding the dynamics of the hair growth cycle and the factors influencing transplantation outcomes can alleviate concerns and set realistic expectations. By partnering with a skilled and experienced surgeon and following postoperative care instructions diligently, patients can maximize their chances of achieving natural-looking, long-lasting results with hair transplantation.