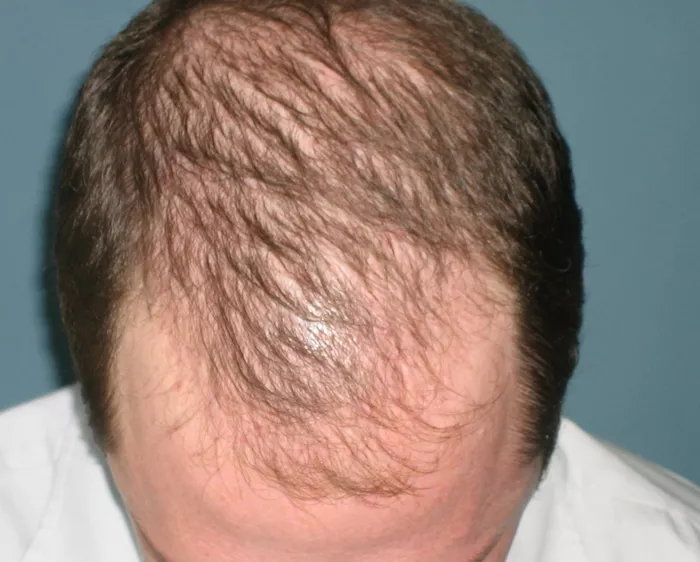
Hair loss is a common concern that affects individuals worldwide, often leading to confusion regarding the terminology used to describe various conditions. Two terms that are frequently interchanged but hold distinct meanings are alopecia and baldness. While both involve the loss of hair, they encompass different underlying causes, manifestations, and treatments. To navigate through this complexity, it is essential to grasp the disparities between alopecia and baldness, as well as recognize their similarities.
Defining Alopecia and Baldness:
Alopecia refers to any form of hair loss, encompassing a broad spectrum of conditions characterized by the partial or complete absence of hair in areas where it typically grows. This umbrella term includes various types of alopecia, such as androgenetic alopecia (pattern baldness), alopecia areata, telogen effluvium, and traction alopecia. Each subtype of alopecia presents with unique features and triggers, ranging from genetic predisposition to autoimmune reactions and external trauma.
Conversely, baldness, often colloquially referred to as “going bald,” specifically denotes the significant and noticeable loss of hair on the scalp, resulting in a visibly barren or sparsely covered head. While baldness can occur as a manifestation of certain types of alopecia, particularly androgenetic alopecia, it is commonly associated with age-related hair thinning and hormonal changes, predominantly in males.
Similarities between Alopecia and Baldness:
Despite their distinctions, alopecia and baldness share several commonalities:
1. Hair Loss: Both conditions entail the shedding or absence of hair from the scalp, leading to changes in appearance and self-perception.
2. Psychological Impact: Hair loss, regardless of its cause, can have profound psychological effects, including diminished self-esteem, anxiety, and depression. Individuals grappling with alopecia or baldness may experience similar emotional challenges associated with changes in their physical appearance.
3. Treatment Options: While treatment approaches vary depending on the specific type and severity of hair loss, both alopecia and baldness may be managed through a range of interventions, including medications, topical treatments, hair transplants, and lifestyle modifications.
Differences between Alopecia and Baldness:
While alopecia and baldness are often used interchangeably, several key distinctions set them apart:
1. Underlying Causes:
- Alopecia: The causes of alopecia are multifactorial and encompass a diverse array of triggers, including genetics, autoimmune responses, hormonal imbalances, medical conditions, and environmental factors. For instance, alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder characterized by the immune system mistakenly attacking hair follicles, leading to sudden hair loss in localized patches.
- Baldness: In contrast, baldness, particularly androgenetic alopecia, is primarily driven by genetic predisposition and hormonal influences, notably dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT, a byproduct of testosterone, binds to hair follicles, causing them to shrink over time and eventually cease producing new hair. This process, known as miniaturization, results in progressive hair thinning and eventual baldness, typically following a distinct pattern, such as a receding hairline or a thinning crown.
2. Patterns of Hair Loss:
- Alopecia: The patterns of hair loss associated with alopecia can vary significantly depending on the subtype and individual characteristics. While some forms of alopecia, such as alopecia areata, may manifest as patchy hair loss confined to specific areas of the scalp or body, others, like telogen effluvium, may involve diffuse shedding of hair across the entire scalp.
- Baldness: Baldness, particularly in males, often follows a predictable pattern known as male pattern baldness or androgenetic alopecia. This pattern typically begins with a receding hairline at the temples, followed by thinning of the hair on the crown and eventual baldness in these areas. Female pattern baldness may also occur but tends to result in diffuse thinning rather than distinct bald patches.
3. Age of Onset and Progression:
- Alopecia: The age of onset and progression of alopecia can vary widely depending on the underlying cause and individual factors. Some forms of alopecia, such as alopecia areata, may manifest suddenly and unpredictably at any age, while others, like androgenetic alopecia, often develop gradually over time, with symptoms typically becoming apparent during adulthood.
- Baldness: Male pattern baldness, the most common form of baldness in men, often begins to manifest in early adulthood and progresses gradually over several decades. In contrast, female pattern baldness may occur later in life and progress more slowly, with hair thinning becoming increasingly noticeable over time.
4. Treatment Approaches:
- Alopecia: Treatment strategies for alopecia vary depending on the specific subtype and underlying causes. In cases of autoimmune-related alopecia, immunosuppressive medications may be prescribed to modulate the immune response and prevent further hair loss. Topical corticosteroids, minoxidil (Rogaine), and other medications may also be used to promote hair regrowth and manage symptoms.
- Baldness: Treatment options for baldness, particularly androgenetic alopecia, typically focus on slowing or halting the progression of hair loss and promoting regrowth. FDA-approved medications such as finasteride (Propecia) and minoxidil are commonly prescribed to inhibit the effects of DHT and stimulate hair follicles. In cases of advanced baldness, hair transplant surgery may be considered to restore hair density and improve aesthetic appearance.
In conclusion, while alopecia and baldness both involve the loss of hair, they represent distinct conditions with unique underlying causes, patterns of hair loss, and treatment approaches. Understanding the differences between these terms is crucial for accurate diagnosis, treatment planning, and management of hair loss disorders. By recognizing the nuances between alopecia and baldness, healthcare professionals and individuals affected by hair loss can make informed decisions regarding appropriate interventions and achieve optimal outcomes.