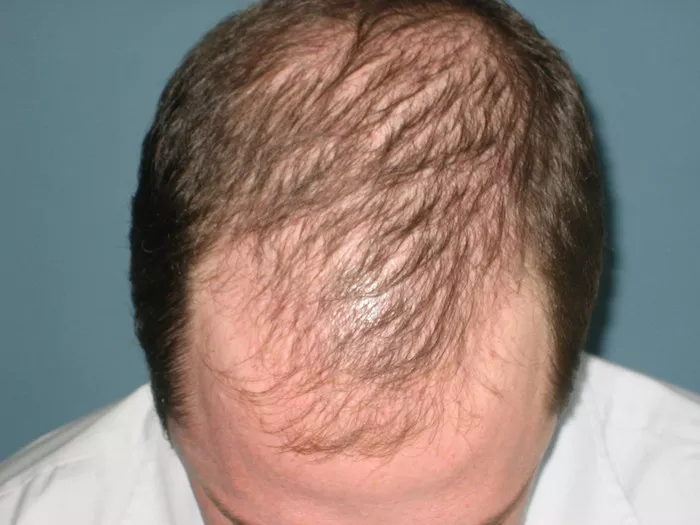
Hair loss, medically termed alopecia, can be a distressing experience for many individuals, especially when it affects the front of the head, a prominent and visible area. While hair loss is commonly associated with aging, it can occur at any stage of life due to a variety of factors. Understanding the underlying causes of hair loss in the front of the head is crucial for effective management and treatment. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the various factors contributing to frontal hair loss and explore potential remedies and preventative measures.
The frontal region of the head, including the hairline and temples, is particularly susceptible to hair loss. This type of hair loss can manifest in different forms, including receding hairlines, thinning hair, and bald patches. While genetics play a significant role in frontal hair loss, other factors such as hormonal imbalances, lifestyle choices, and underlying medical conditions can also contribute to this condition.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetic predisposition, or hereditary hair loss, is the most common cause of hair loss in the front of the head. This condition, known as male or female pattern baldness, is primarily determined by genes inherited from both parents. In men, male pattern baldness typically presents as a receding hairline and thinning crown, while women may experience diffuse hair thinning across the frontal scalp.
The primary culprit in hereditary hair loss is dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a byproduct of testosterone metabolism. DHT binds to hair follicles, causing them to shrink over time, leading to shorter and finer hair growth. This process, known as miniaturization, eventually renders the affected follicles unable to produce visible hair, resulting in baldness.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal imbalances can also contribute to hair loss in the front of the head. Fluctuations in hormone levels, particularly androgens such as testosterone and its derivatives, can impact hair follicle function and growth cycles. Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) in women and hormonal fluctuations associated with menopause can lead to hair thinning and frontal hair loss.
Additionally, thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, can disrupt hormonal balance and contribute to hair loss. Thyroid hormones play a crucial role in regulating metabolism, and alterations in thyroid function can affect hair growth cycles, leading to thinning and shedding in the frontal scalp area.
Stress and Lifestyle Factors
Chronic stress and unhealthy lifestyle habits can take a toll on overall health, including the condition of the hair. Stress triggers the release of hormones such as cortisol, which, when elevated over prolonged periods, can disrupt hair follicle function and lead to hair loss. Moreover, poor dietary choices, inadequate nutrition, and excessive consumption of alcohol and tobacco can deprive the scalp of essential nutrients, impairing hair growth and contributing to frontal hair loss.
Poor Scalp Health
The health of the scalp is crucial for maintaining strong and healthy hair. Conditions such as dandruff, scalp infections, and inflammation can compromise hair follicle function and impede proper hair growth. In particular, conditions like seborrheic dermatitis, characterized by red, itchy, and flaky skin, can affect the frontal scalp area and exacerbate hair loss.
Furthermore, excessive use of hairstyling products, heat styling tools, and harsh chemical treatments can damage the hair shaft and weaken the follicles, leading to breakage and thinning in the front of the head. It is essential to maintain good scalp hygiene and minimize exposure to damaging agents to preserve hair health.
Medical Conditions and Treatments
Certain medical conditions and treatments can trigger hair loss, including chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and autoimmune diseases. Chemotherapy drugs target rapidly dividing cells, including those in hair follicles, leading to temporary hair loss known as chemotherapy-induced alopecia. Similarly, radiation therapy aimed at cancerous tumors in the head and neck region can damage hair follicles and result in localized hair loss.
Autoimmune diseases such as alopecia areata involve the immune system mistakenly attacking the hair follicles, resulting in patchy hair loss across the scalp, including the frontal area. Other autoimmune conditions like lupus can also cause hair thinning and loss in a diffuse pattern.
Prevention and Treatment Options
While some causes of frontal hair loss, such as genetic predisposition, cannot be prevented, several strategies can help minimize further hair loss and promote regrowth:
1. Healthy Lifestyle: Adopting a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, staying hydrated, and managing stress through relaxation techniques can support overall hair health.
2. Scalp Care: Maintain good scalp hygiene by regularly washing with a gentle shampoo and avoiding excessive use of styling products and heat styling tools.
3. Medical Treatments: Medications such as minoxidil and finasteride are FDA-approved for treating hereditary hair loss and may help slow down hair thinning and promote regrowth.
4. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP therapy involves injecting concentrated platelets from the patient’s blood into the scalp to stimulate hair follicle regeneration and promote hair growth.
5. Hair Transplantation: Surgical hair restoration techniques such as follicular unit transplantation (FUT) and follicular unit extraction (FUE) can effectively restore hair density in the frontal scalp by transplanting healthy hair follicles from donor areas.
6. Lifestyle Modifications: Avoiding tight hairstyles, minimizing exposure to harsh chemicals and pollutants, and protecting the scalp from excessive sun exposure can help prevent further damage to the hair.
Conclusion
Hair loss in the front of the head can have significant psychological and emotional implications for affected individuals. Understanding the underlying causes of frontal hair loss is essential for implementing targeted treatment strategies and preventing further progression of the condition. By addressing genetic predisposition, hormonal imbalances, scalp health, and lifestyle factors, individuals can take proactive steps to preserve hair health and maintain a fuller, more youthful appearance. Additionally, seeking guidance from dermatologists or hair restoration specialists can provide personalized treatment plans tailored to individual needs, ultimately restoring confidence and well-being.