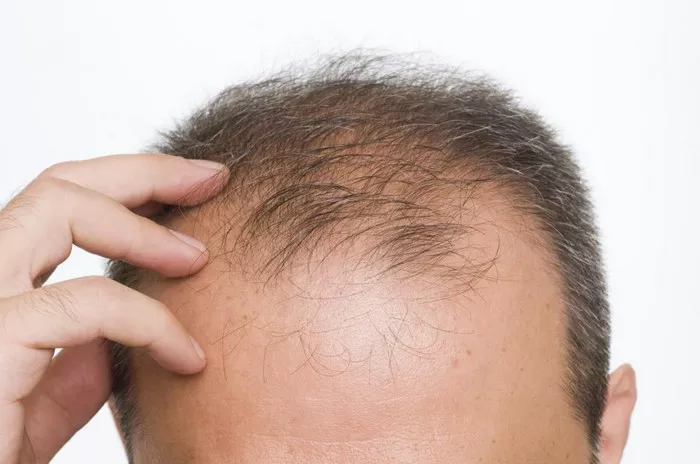
Hair thinning is a common concern that affects millions of people worldwide. While it is often associated with aging, it can occur at any stage of life and may be indicative of underlying health issues. Understanding what hair thinning means, its causes, symptoms, and available treatment options is crucial for effectively managing this condition and restoring confidence in individuals experiencing it.
What is Hair Thinning?
Hair thinning, also known as hair loss or alopecia, refers to a reduction in the density and diameter of hair strands, leading to a visibly thinner appearance of the hair. It can occur gradually over time or suddenly, depending on the underlying cause. Hair thinning can affect both men and women and may occur on the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, or other parts of the body where hair grows.
Causes of Hair Thinning
Hair thinning can be attributed to various factors, including genetics, hormonal changes, medical conditions, and lifestyle factors. Understanding the underlying cause is essential for determining the most appropriate treatment approach. Some common causes of hair thinning include:
1. Genetics: Hereditary hair loss, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is the most common cause of hair thinning. It typically manifests as a receding hairline in men and diffuse thinning on the crown of the scalp in both men and women.
2. Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those occurring during pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, or thyroid disorders, can contribute to hair thinning. Imbalances in hormones like testosterone, estrogen, and thyroid hormones can affect the growth cycle of hair follicles.
3. Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as alopecia areata, scalp infections, autoimmune diseases, and nutritional deficiencies, can lead to hair thinning. Chronic illnesses, like diabetes and lupus, can also impact hair health.
4. Stress: Physical or emotional stress can disrupt the normal hair growth cycle, leading to increased shedding and hair thinning. Conditions like telogen effluvium can result from stressors such as surgery, illness, or significant life events.
5. Diet and Nutrition: Poor nutrition, particularly deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals like iron, zinc, and vitamin D, can affect hair health and contribute to thinning. A balanced diet rich in nutrients is vital for maintaining healthy hair growth.
6. Medications and Treatments: Certain medications, such as chemotherapy drugs, antidepressants, blood thinners, and hormonal contraceptives, can cause hair thinning as a side effect. Radiation therapy and some medical treatments can also impact hair follicles.
Symptoms of Hair Thinning
Recognizing the signs of hair thinning is essential for early intervention and treatment. Some common symptoms include:
1. Increased Shedding: Noticeable hair loss during brushing, showering, or styling, leading to a visible reduction in hair density.
2. Thinning Hair: Gradual thinning of the hair, particularly along the part line or crown of the scalp, which may be more pronounced in certain areas.
3. Bald Patches: Formation of bald patches or areas of visibly reduced hair density, which may indicate conditions like alopecia areata.
4. Changes in Hair Texture: Changes in the texture of the hair, such as increased brittleness, dryness, or loss of shine, which can accompany hair thinning.
5. Scalp Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity or discomfort of the scalp, often accompanied by itching, irritation, or inflammation.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Seeking professional medical advice is essential for diagnosing the underlying cause of hair thinning and determining the most appropriate treatment plan. A dermatologist or trichologist can conduct a thorough evaluation, which may include:
1. Medical History: Discussion of personal and family medical history, including any underlying health conditions, medications, or recent life events.
2. Physical Examination: Examination of the scalp and hair follicles to assess hair density, pattern of thinning, and presence of any scalp abnormalities.
3. Diagnostic Tests: Blood tests to evaluate hormone levels, nutritional status, thyroid function, and markers of inflammation or autoimmune disorders.
4. Scalp Biopsy: In some cases, a biopsy of the scalp tissue may be recommended to examine hair follicles under a microscope and assess for underlying pathology.
Treatment Options
The treatment approach for hair thinning depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Some common treatment options include:
1. Topical Medications: Over-the-counter or prescription topical treatments, such as minoxidil (Rogaine), can help stimulate hair growth and prevent further thinning.
2. Oral Medications: Prescription medications like finasteride (Propecia) may be recommended for men with androgenetic alopecia to inhibit the production of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone linked to hair loss.
3. Hormone Therapy: Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may be prescribed for women experiencing hair thinning due to hormonal imbalances, such as menopause or thyroid disorders.
4. Nutritional Supplements: Supplements containing vitamins, minerals, and essential nutrients for hair health, such as biotin, iron, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids, may be recommended to address nutritional deficiencies.
5. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP therapy involves injecting concentrated platelets from the patient’s blood into the scalp to stimulate hair follicle regeneration and promote hair growth.
6. Hair Transplant Surgery: In cases of advanced hair loss, hair transplant surgery, such as follicular unit transplantation (FUT) or follicular unit extraction (FUE), may be considered to transplant healthy hair follicles from donor areas to thinning or balding areas of the scalp.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
In addition to medical treatments, certain lifestyle modifications and home remedies may help improve hair health and reduce thinning:
1. Healthy Diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in protein, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can support overall hair health and growth.
2. Stress Management: Practicing stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help minimize the impact of stress on hair health.
3. Gentle Hair Care: Avoiding harsh hair treatments, excessive heat styling, and tight hairstyles can prevent damage to hair follicles and minimize hair thinning.
4. Scalp Massage: Regular scalp massage with essential oils or massaging devices can stimulate blood flow to the scalp and promote hair growth.
5. Avoiding Smoking and Excessive Alcohol: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can impair circulation and contribute to hair loss, so quitting smoking and moderating alcohol intake may help improve hair health.
Conclusion
Hair thinning can have a significant impact on an individual’s self-esteem and quality of life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options is crucial for effectively managing this condition and promoting hair regrowth. By seeking professional medical advice, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, and exploring appropriate treatment modalities, individuals experiencing hair thinning can regain confidence and achieve healthier, fuller-looking hair. Remember, addressing hair thinning early can lead to better outcomes, so don’t hesitate to seek help if you notice changes in your hair density or texture.