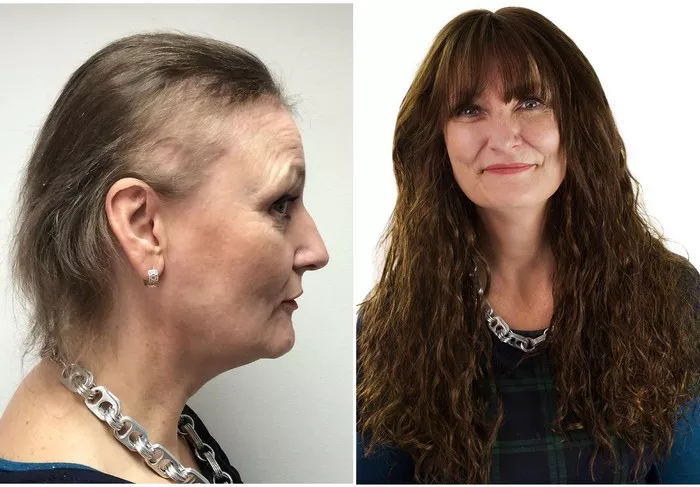
Hair is often considered a significant aspect of a woman’s identity, reflecting health, vitality, and beauty. However, for many women, thinning hair can be a source of concern and distress. While it’s normal to lose some hair daily, excessive hair shedding or noticeable thinning can indicate an underlying issue that requires attention. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of female thinning hair, exploring its appearance, causes, and potential solutions.
Recognizing the Signs of Thinning Hair in Women
Thinning hair in women may manifest in various ways, often presenting as changes in hair density, texture, and overall appearance. Here are some common signs to look out for:
1. Increased Hair Shedding: One of the earliest signs of thinning hair is excessive shedding, noticeable during activities like washing, brushing, or styling. While shedding up to 100 hairs per day is considered normal, exceeding this amount could indicate a problem.
2. Widening Part: As hair begins to thin, the parting in the hair may widen, revealing more of the scalp than usual. This widening can be a gradual process, but it’s often a noticeable change for individuals experiencing thinning hair.
3. Decreased Volume: Thinning hair tends to lack volume and density, resulting in a limp or flat appearance. Hair may appear finer and less substantial, making it challenging to achieve desired hairstyles.
4. Visible Scalp: In advanced cases of thinning hair, the scalp becomes more visible, especially around the crown and temples. This visibility is often more pronounced in certain lighting conditions or when hair is styled in specific ways.
5. Changes in Hair Texture: Thinning hair may feel finer, softer, or more brittle than usual. Additionally, some individuals may notice changes in curl pattern or overall texture as hair density decreases.
6. Slow Hair Growth: While not always immediately apparent, slow or stunted hair growth can be a sign of underlying issues contributing to thinning hair. Hair may take longer to grow or appear stagnant in its growth phase.
Understanding the Causes of Thinning Hair in Women
Thinning hair in women can stem from a multitude of factors, ranging from genetics to hormonal imbalances and lifestyle choices. Understanding the underlying causes is crucial for effectively addressing and managing thinning hair. Here are some common culprits:
1. Genetics: Hereditary hair loss, also known as female pattern hair loss or androgenetic alopecia, is the most common cause of thinning hair in women. It’s characterized by a gradual thinning of hair, typically starting at the crown or part line.
2. Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels, particularly during pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, or as a result of hormonal disorders like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can contribute to thinning hair. Androgen hormones, such as testosterone and its derivative dihydrotestosterone (DHT), play a role in hair thinning by shrinking hair follicles over time.
3. Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions and illnesses can lead to hair thinning as a secondary symptom. Conditions such as thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases, alopecia areata, and scalp infections can disrupt the hair growth cycle and cause excessive shedding.
4. Nutritional Deficiencies: Inadequate intake of essential nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, and proteins, can impact hair health and lead to thinning. Iron deficiency anemia, in particular, is associated with hair loss in women.
5. Stress and Lifestyle Factors: Chronic stress, poor dietary habits, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and extreme weight loss can all contribute to hair thinning by disrupting the body’s natural processes and affecting hair follicle function.
6. Medications and Treatments: Certain medications and medical treatments, including chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and some prescription drugs for conditions like hypertension, depression, and acne, can cause hair thinning as a side effect.
Exploring Solutions for Thinning Hair in Women
While dealing with thinning hair can be challenging, several strategies and treatments can help improve hair density and overall hair health. The most suitable approach depends on the underlying cause of thinning and individual preferences. Here are some potential solutions to consider:
1. Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter topical treatments containing minoxidil, a vasodilator, can help stimulate hair growth and improve hair density in some women with hereditary hair loss. These treatments are typically applied directly to the scalp once or twice daily.
2. Prescription Medications: For women experiencing androgenetic alopecia, healthcare providers may prescribe medications like spironolactone or oral contraceptives containing anti-androgenic properties to help block the effects of androgens on hair follicles.
3. Nutritional Supplements: Supplements containing essential nutrients for hair health, such as biotin, iron, zinc, and vitamin D, may be beneficial for women with nutritional deficiencies contributing to hair thinning. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements.
4. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP therapy involves injecting a concentrated solution of the patient’s own platelets into the scalp to stimulate hair growth and improve hair thickness. While more research is needed to confirm its efficacy, some women may find PRP therapy helpful for treating thinning hair.
5. Hair Transplantation: In cases of advanced hair loss, hair transplantation procedures, such as follicular unit transplantation (FUT) or follicular unit extraction (FUE), can be performed to transplant healthy hair follicles from donor areas to thinning or balding areas of the scalp.
6. Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can promote overall hair health and reduce the risk of further hair thinning. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, managing stress effectively, avoiding harsh hair treatments, and practicing good hair care habits.
7. Cosmetic Solutions: Various cosmetic options, such as volumizing hair products, hair fibers, hairpieces, and wigs, can help conceal thinning hair and improve overall appearance. These solutions offer immediate results while other treatments work to address the underlying causes of thinning.
Conclusion
Thinning hair is a common concern for many women, impacting self-esteem and quality of life. By recognizing the signs and understanding the underlying causes, women can take proactive steps to address thinning hair and restore hair density and confidence. Whether through topical treatments, prescription medications, nutritional supplements, or cosmetic solutions, there are various options available to help women effectively manage thinning hair and achieve healthier, fuller-looking locks. Consulting with a healthcare professional or dermatologist can provide personalized recommendations and guidance tailored to individual needs and concerns. With the right approach and support, women can embrace their hair journey with confidence and vitality.
FAQs
Q1: How do I know when my hair is thinning?
Hair thinning can manifest in various ways, but some common signs include increased shedding, widening of the part line, a decrease in hair density, and a noticeable reduction in hair volume. You may observe more hair fall during activities like showering or brushing, and your scalp may become more visible through your hair. Additionally, noticing shorter hairs or finer texture in areas where your hair was once fuller could indicate thinning.
Q2: At what age does women’s hair start thinning?
Hair thinning in women can occur at different ages depending on various factors such as genetics, hormonal changes, lifestyle, and overall health. While it’s more commonly associated with aging, women can experience thinning hair as early as their 20s or 30s due to factors like hormonal imbalances, stress, nutritional deficiencies, or certain medical conditions. However, it becomes more prevalent with advancing age, typically occurring around menopause due to hormonal shifts.
Q3: Can you see your scalp when your hair is thinning?
Yes, seeing the scalp through the hair is a common indication of thinning. As hair follicles become less dense or miniaturized, the scalp becomes more visible, especially in areas where the hair is sparse or has thinned significantly. This increased visibility of the scalp can occur anywhere on the head, including the crown, temples, or along the part line.
Q4: Can hair recover from thinning?
Hair thinning can sometimes be reversible, especially if addressed early and appropriately. Treatment options vary depending on the underlying cause of thinning, which could include lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, medical treatments, or topical solutions. However, it’s essential to manage expectations, as some forms of hair thinning, particularly those influenced by genetics or irreversible factors, may not fully recover. Nonetheless, with proper care and intervention, it’s possible to slow down or even halt further thinning and promote healthier hair growth. Consulting with a dermatologist or trichologist can provide personalized recommendations for addressing hair thinning effectively.